
Individuals with Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB) require specialized handling and care to prevent new blister formation, reduce pain and infection risk, and address the broader medical challenges associated with the condition.
For background on EB types, subtypes, and key clinical features, see Understanding EB Types.
Handle With Care
Even routine activities and minimal trauma can trigger new blisters, making prevention a critical part of clinical care. The following are some of the most frequent causes of blisters professionals should be aware of:
⚠️ NO FRICTION: e.g.,rubbing, sliding, firm handling of skin, abrasive clothing or sheets
⚠️ NO ADHESIVES: e.g., medical tape, Band-Aids®, or unmodified monitor leads.
⚠️ NO PRESSURE: e.g., tight clothing/shoes, BP cuffs, tourniquets.
⚠️ NO HEAT: e.g., prolonged warm or humid environments.
🚫 DO NOT USE ADHESIVE TAPE OR REGULAR BANDAIDS. Adhesives directly on skin cause trauma.
EB in Clinical Settings
Infection Prevention
EB wounds are prone to Staph and Pseudomonas. Recognize and treat infection promptly. Watch for redness, pus, odor, or fever. Culture when suspicious.
Pain and Itch
Control discomfort while minimizing opioids. Use short-term analgesics; antihistamines can reduce itching. Prevent constipation if opioids are used.
Proper care adaptations are vital to preventing injury, reducing pain, and promoting quality of life for individuals with EB. Apply these fundamentals in any setting to promote safe, effective, and compassionate EB care.
- Prevent shear and friction injuries from the first touch.
- Always lift patients rather than slide.
- Infants should not be fully undressed for exams.
- Use padding or tubular gauze to protect high-friction areas.
- Select and secure dressings without adhesives.
- Never apply adhesives directly to the skin.
- Use non-adherent dressings (i.e., EB-Friendly Dressings List).
- Remove adhesives from monitors or apply over silicone/hydrogel barriers.
- Add padding over high-risk pressure points.
EB blisters are not self-limited; once they form, they often continue to enlarge unless they are drained and protected. Follow these step-by-step recommendations for safe lancing here.
Guidelines for Safe Blister Drainage
- Wash hands and assemble supplies.
- Use a sterile needle or lancet to lance tense blisters over dime size.
- Gently push the fluid to one corner of the blister.
- Prick 1–2 holes on the side (not top) of the blister.
- Drain fluid with gauze or Q-tip, keeping the blister roof intact.
- Reuse the lancet only if there are no signs of infection (white or cloudy drainage).
- Apply ointment → non-adherent dressing → rolled gauze or netting to secure.
🚫 DO NOT USE ADHESIVE TAPE OR REGULAR BANDAIDS. In an incident where adhesives have been applied, leave in place until patient is stable. Use adhesive removal spray or emollient to gently loosen and carefully remove adhesives to minimize trauma. Alternatives include Vaseline®, mineral oil, coconut oil, normal saline, baby oil, or tap water.
- Use gentle technique to avoid trauma.
- Cleanse by dabbing, not rubbing.
- Place tourniquets over gauze or bandage.
- Give vaccines as usual; apply light pressure, not massage.
Refer to Emergency Management for EB for detailed recommendations.
- Disperse cuff pressure to protect fragile skin.
- Wrap gauze or clothing under the cuff; never apply directly to skin.
Refer to Emergency Management for EB for detailed recommendations.
- Recognize and treat infection promptly.
- EB wounds are prone to bacterial infection (Staph, Pseudomonas).
- Look for redness, pus, odor, honey-colored crusts, fever, or chills.
- Culture when suspicious; systemic cases require labs and blood cultures.
- Control discomfort while avoiding opioid complications.
- Manage acute pain with analgesics; limit long-term narcotics.
- Antihistamines can reduce itching.
- Prevent constipation if opioids are used.
- Address swallowing issues and maintain high-calorie intake.
- Dysphagia, strictures, and constipation are common.
- Dietitian involvement is essential.
- Encourage soft, high-protein foods and supplements.
- Assess the full esophagus; balloon dilatation may be needed.
- Monitor for chronic anemia and nutrient loss.
- Iron supplementation is often required.
- Check selenium and carnitine levels when indicated.
- Reduce friction through soft, seamless garments.
- Avoid seams, tags, and tight waistbands.
- Choose loose, padded shoes with rubber soles.
- Pad diapers and waistbands.
- Keep skin cool and dry to prevent new blistering.
- Avoid heat and humidity.
- Use body-temperature or cooler water.
- Maintain air-conditioned environments when possible.
- Pad diapers and waistbands.
Specialized Procedures & Hospital-Based Care
When patients with EB require diagnostic tests, surgery, or hospitalization, standard medical practices often need careful modification. From anesthesia and surgical positioning to EEGs, sleep studies, and IV access, clinicians must take extra precautions to protect fragile skin and mucosa. This section highlights the most important adaptations for safe hospital- and procedure-based care.
EEG Placement Guide for EB >
Instructions for safe EEG electrode application on fragile skin, including modified materials, placement steps, and precautions to prevent skin breakdown.
Sleep Study Protocol for Patients with EB >
Steps for safely conducting polysomnography on patients with EB or other fragile‑skin conditions, emphasizing minimal adhesives, gentle cleansing, and alternative lead placement and securing methods. and procedure-based care.
Emergency Care Management >
Refer to our emergency care guide for EB offering protocols for extreme skin fragility, airway and IV management, and surgical preparation. Emphasizes using silicone dressings, avoiding adhesives, gentle handling, and tailoring care to each patient
Comprehensive Care Guides
Affecting multiple body systems, mobility, and overall quality of life, Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB) requires close collaboration across specialties and a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach to care. Explore the topics below for clinical guidance and practical information that support consistent, coordinated care across all systems affected by EB.
 Anemia
Learn More
Anemia
Learn More
 Cancer
Learn M ore
Cancer
Learn M ore
 Constipation
Learn More
Constipation
Learn More
 Daily Living
Learn More
Daily Living
Learn More
 Eye Care
Learn More
Eye Care
Learn More
 Foot Care
Learn More
Foot Care
Learn More
 Hand Surgery & Therapy
Learn More
Hand Surgery & Therapy
Learn More
 Nutrition & Feeding Support
Learn More
Nutrition & Feeding Support
Learn More
 Occupational & Physical Therapy
Learn More
Occupational & Physical Therapy
Learn More
 Oral Health
Learn More
Oral Health
Learn More
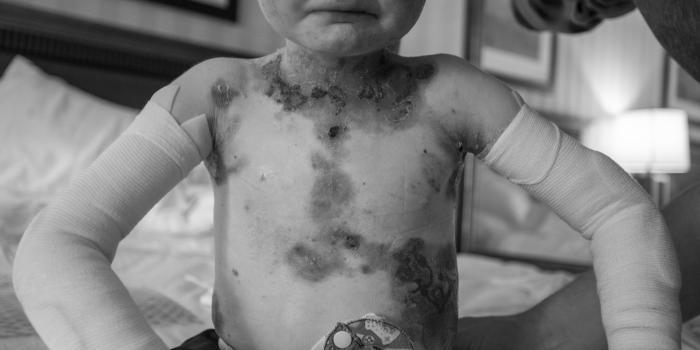 Pain & Itch
Learn More
Pain & Itch
Learn More
 Palliative Care
Learn More
Palliative Care
Learn More
 Pregnancy & Childbirth
Learn More
Pregnancy & Childbirth
Learn More
 Psychosocial Care
Learn More
Psychosocial Care
Learn More
 Sexuality
Learn More
Sexuality
Learn More
The information provided herein is intended to educate the reader about certain medical conditions and certain possible treatments. It is not a substitute for examination, diagnosis, and medical care provided by a licensed and qualified health professional. If you believe you, your child, or someone you know, suffer from conditions described herein, please see your healthcare provider. Do not attempt to treat yourself, your child, or anyone else without proper medical supervision.



